
If you’ve heard of blockchain, you’ve likely heard of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) and protocols build on top of them like zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs. You may have also heard of zkLocus, which leverages these technologies to turn geolocation data into a Real World Asset (RWA) on-chain, and enable private and verifiable geolocation sharing. The Ethereum roadmap is strongly focused on integrating ZKP constructs into the core protocol. The Mina Blockchain is nearing the mainnet launch of programmable recursive zkSNARKs, while Polygon Maiden is using zkSTARKs to abstract the familiar von Neumann architecture into a Zero-Knowledge Virtual Machine (ZKVM).
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs, exploring their potential to enable a novel realm of software on which we can build the technology of tomorrow. We will compare the Verifiable Computation Model (VCM) enabled by these ZKP constructs with the traditional model employed by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), highlighting the limitations of the latter and the advantages of the former.
We’re also going to expand on the VCM definition and break it down into two distinct areas: the Linear Verifiable Computational Model (LVCM) and the Constant Verifiable Computational Model (CVCM). These are definitions that I have conceived while formulating the value-proposition of Zero-Knowledge (ZK) protocols like zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs from a practical perspective.
The LVCM is the one that the EVM uses, and it comes with limitations. The time it takes to verify a computation grows linearly with the number of instructions in the smart contract. That means the more complex the contract, the longer it takes to verify. We will explore how this limits the scalability of the EVM, and you will understand why ZKPs have been explicitly introduced into the Ethereum roadmap.
On the other hand, the CVCM is the one used by zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs use, and it addresses the limitations of the EVM. While the time that it takes to perform a computation is still linear with the computation size, the time it takes to verify it is constant, regardless of how complex the underlying computation is. Such a model is inherintely scalable, as it allows to chain several computations together and verifying them all at the same time, in a constant time, cost, and size.
By breaking down the VCM into these two models, we are able to succintly highlight the value proposition of zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs from a practial perspective
This article is written based on learnings from developing zkLocus - a pioneering Zero-Knowledge, on-chain, cross-chain, and off-chain protocol, offering a disruptive paradigm in private and verifiable geolocation sharing. It allows users to authenticate their presence in specific geographical areas without revealing exact coordinates. zkLocus brings geolocation data onto the blockchain. It offers native bridging, native rollup functionality, and infinite proof compression. zkLocus is built on recursive zkSNARKs, making it inherently open to customization and extension.
You can find more about zkLocus at the following links:
- zklocus.dev - The official website of zkLocus. Here you can find the latest updates about zkLocus and contact information.
- GitHub/zkLocus - The GitHub repository of zkLocus. Here you can find the source code of zkLocus.
- x.com/zkLocus - The Twitter/X account of zkLocus. Here you can find the latest updates about zkLocus.
- zkLocus Whitepaper - The whitepaper of zkLocus. Here you can find a detailed description of zkLocus and its underlying technology.
- zkSafeZones Whitepaper - The whitepaper of zkSafeZones. Here you can find the whitepaper for our intiative aiming at safeguarding civilians in conflict zones, and sets the groundwork for enforcement of the law on-chain.
- contact@zklocus.dev - The email address of zkLocus. Here you can contact the zkLocus team.
Verifiable & Non-Verifiable Computing

Recursive zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs enable a novel verifiable computation model that is infinitely scalable and constant in time, cost, and size. But what exactly does it mean for a computation to be verifiable? How that model differ from traditional Web 2 applications written in languages like JavaScript, Python, or Java? Can we have a verifiable computation model that does not utilize Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP)?
It’s important to answer all of these and other questions in order to understand the value proposition of Zero-Knowledge Proof protocols like zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs, as well blockchains that are built on top of them, like Mina Protocol. Throughout this section, we will explore the differences between “traditional” non-verifed computation models and verifiable computation models, and later how zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs enable the latter.
Non-Verifiable Computation Model (NCM)
In a Non-Verifiable Computation Model (NCM), the computation is performed by a single or a group of entities, and the result is shared with other entities. The other entities have no way of verifying that the computation was performed correctly. They must trust the entity that performed the computation. This trust is often misplaced, as the entity may have an incentive to manipulate the result of the computation in their favor.
The vast majority of computer programs are implemented under this model. In order to understand what that means, let’s explore an example. Suppose you are going to implement a social networking platform, where users can post messages and interact with each other. You implement it using your programming language and framework of choice, such as Python & Django, JavaScript, NodeJS & React or Java & Spring. You deploy the application to a server, and users can access it through a web browser.
You pinky-promise to the users that you will not store their messages and that you will not share their data with third-parties. However, there is nothing enforcing that. The users must trust you, and you may lie, whether accidentally or deliberately. Open-sourcing your product does not solve the problem, as there is nothing ensuring that the deployed version of the application is the same as the open-sourced one.
Verifiable Computation Model (VCM)
Contrasting with Non-Verifiable Computation Model is the Verifiable Computation Model (VCM). In this model, there is a way to prove that the computation was performed by exclusively executing a pre-defined set of instructions. In other words, it is possible to prove that a particular piece of code was executed, without any tampering in the process.
Smart contracts on blockchains like Ethereum, Mina, and Polygon are examples of applications that utilize the Verifiable Computation Model. The smart contract contains instructions to execute on the blockchain state and updates to that state. For a smart contract execution to be accepted and applied on the blockchain, the participants of the blockchain network must reach a consensus that the execution was valid. This consensus is only reached if the execution was performed correctly, precisely according to the instructions in that smart contract and blockchain state.
If you were to implement your social networking platform using smart contracts on the blockchain, your users would no longer need to trust you, but rather the blockchain network. Since the network only accepts a smart contract execution transaction if the instructions in that smart contract were executed verbatim, we can say that the computation is verifiable.
The Etherum Virtual Machine’s (EVM) Verifiable Computation Model

As mentioned previosly, the EVM enables a Verifiable Computation Model, where the execution of smart contracts, alongside their inputs (smart contract function arguments and existing blockchain state), outputs (blockchain state updates) is cryptographically attested. This is achieved by having network participants (validators) re-execute the smart contract on their own machines and compare the result with the result of the original execution. If the results match, the execution is considered valid and is applied to the blockchain state. If the results do not match, the execution is considered invalid and is rejected. Anyone can verify whether a particular smart contract execution was valid by re-executing the smart contract on their own machine and comparing the result with the result of the original execution.
You can think of it as a “brute-force” approach at verifiable computation. In order to verify if a claimed smart contract execution is correct, you re-execute it yourself and compare the result with the result of the claimed execution. If the results match, the claimed execution is correct. If the results do not match, the claimed execution is incorrect. If the smart contract has 10 instructions, you’ll need to re-execute those 10 instructions on your own machine, if the smart contract has 100 instructions, you’ll need to re-execute those 100 instructions on your own machine, and so on. This verification process needs to be performed by all validators in the network.
A naive implementation of this verifiable computation model leaves the blockchain network vulnerable to a Denial of Service (DoS) attack. An attacker can deploy a smart contract with a large number of instructions, forcing validators to re-execute those instructions, and thus slowing down or taking down the network. Ethereum solves problem in two ways: by charging gas fees for smart contract execution and by limiting the number of instructions in a smart contract. The gas fees ensure that the attacker pays for the computational resources they consume, while the instruction limit ensures that the attacker cannot consume an excessive amount of computational resources.
Public & Private Data On EVM
The EVM’s Verifiable Computation Model is limited to public data. This means that the inputs to a smart contract execution, the smart contract function arguments, and the existing blockchain state must be public. This is because the validators need to re-execute the smart contract on their own machines, and they cannot do that if the inputs are private. For example, if a smart contract execution involves a private key or a secret value known only to the transaction submitter, the validators cannot re-execute the smart contract on their own machines, as they do not have access to the private key or that value. This limitation makes it impossible to execute smart contracts that involve private data, such as personal information, financial information, and encryption keys.
Limitations
The Ethereum Virtual Machine’s (EVM) Verifiable Computation Model has several limitations:
-
Limited Complexity: The most obvious limitation of the EVM’s VCM is the limited size & time complexity of computer programs (smart contracts) whose execution can be verfied under the VCM. The strict gas fee limits make it impossible to execute complex programs on the EVM. For example, it is not possible to run a complex algorithm for several hours or days and submit the result of that execution to the blockchain. Examples of such algorithms include machine learning models, simulations, predictions and games.
-
Limited Scalability: Due to the constraint of having to re-execute the entire smart contract on all validators’ machines, the EVM’s VCM scalability is limited. This is caused by the redundancy of the execution: not only the transaction submitter must execute the smart contract, but all validators must do so as well.
-
Energy Inefficiency: The EVM’s VCM is energy inefficient, as it requires all validators to re-execute the smart contract on their own machines. This is a waste of computational resources, as the smart contract execution is already performed by the transaction submitter. If we assume that the execution of a smart contract to have cost
Kenergy units, then the total energy cost of the smart contract execution on the EVM isN * K + 1, whereNis the number of validators, and1is the initial execution by the transaction submitter. -
Limited Privacy: In the EVM’s VCM the computation is performed on public data. This means that all of the execution inputs, outputs, and intermediate states are publicly visible. This is a significant limitation, as it makes it impossible to perform computations on private data, such as personal information, financial information, and encryption keys.
zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs: A Novel Verifiable Computation Model

Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP) enable one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that a statement is true, without revealing any information about the statement itself. zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs are two types of Zero-Knowledge Proofs that are used in blockchain applications to enable a novel verifiable computation model, which addresses the limitations of the EVM’s Verifiable Computation Model.
zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs
zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs are cryptographic protocols built using Zero-Knowledge Proofs that enable a prover to prove to a verifier that a computation was performed correctly, without revealing the computation itself. zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs are used in blockchain applications to enable a novel verifiable computation model, which is infinitely scalable, constant in time, cost, and size, and private.
While there are differences between zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs, they are of little relevance for the purpose of this article. As such, we will use the term zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs interchangeably.
For a detailed and practial explanation of zkSNARKs consult my article covering zkSNARKs. It iteratively explains the concept of zkSNARKs, starting from the basics of Zero-Knowledge Proofs(ZKP), then using this knowledge to explain zkSNARKs, then diving into recursively composing zkSNARKs, and finally with a practical implementation of a zkSNARK calculator using O1JS.
zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs: Observation Of A Computation
Unlike in the EVM Verifiable Computation Model, where the validators re-execute the smart contract on their own machines, in the zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs Verifiable Computation Model, the prover generates a proof that the computation was performed correctly, and the verifier verifies that proof. The verifier does not need to re-execute the computation on their own machine, as the proof is sufficient to attest to the correctness of the computation, alongside all of its inputs and outputs.
In this sense, a zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs proof represents a cryptographic observation of a computation. The prover generates the proof, and the verifier verifies the proof:
- The prover is the entity submitting the smart contract execution transaction onto the blockahin. It does so, by generating a proof of execution.
- The verifier is the network participant that validates the transactions submitted on-chain. It does so, by verifying the proof of the execution submitted by the prover.
- The proof is the cryptographic observation of the computation, generated by the prover. This proof encompasses the correct execution of the smart contract, alongside all of its inputs and outputs.
- The verification is the process of validating the proof, performed by a verifier or any other network participant. The verification can be performed in approximately constant time, cost, and size, regardless of the complexity of the underlying computation.
As such, zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs enable a VCM by producing a cryptographic proof of an ovservation of a computation, alongside all of its inputs and outputs. To verify the correctness of the computation, it’s not necessary to re-execute the whole computation, but to only verify the proof of the observation of that computation. In general terms, verifying the proof is faster than generating the proof.
Run Once, Prove Everywhere
The zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs Verifiable Computation Model is based on the principle of “run once, prove everywhere”. This means that the computation is performed once by the prover, and the proof of that computation is verified by the verifiers. The prover does not need to re-execute the computation for each verifier, as the proof itself is sufficient to attest to the correctness of the computation. This is in contrast to the EVM Verifiable Computation Model, where the computation is re-executed by all validators. Given that the verification of the proof is faster than the generation of the proof, this model brings several advantages over the EVM-based architecture.
Shifting The Workload To The Client-Side
While in the EVM the workload is equally distributed between the participants of the consensus protocol, in the zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs Verifiable Computation Model the workload is shifted to the client-side (the prover). The vast majority of the energy consumption happens on the client’s/prover’s side, during the generation of proof of the observation of the computation.
Proof Of Everything
Proof of everything is a term coined by Will Cove, the Head of Community at Mina Foundation. It enables a practial mental model for looking at the Verifiable Computation Model provided by zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs. The idea is that users (clients) generate proofs of computations on their local devices, and then share those with the desired entities (verifiers). The data on which the proofs are generated can remain fully private, without ever leaving the client’s device.
When the zkSNARK/zkSTARK VCM with the blockchain, those proofs are shared with the blockchain consensus participants. In the case of the Mina blockchain, you can think of the blockchain as the verifier, and the clients submitting transactions as the provers. Each proof is a cryptographic observation of a computation, alongside all of the inputs (both public and private) and changes to the on-chain state (outputs).
Recursive zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs
While the concept of being able to produce an ovservation of a computation is powerful, it would be very limited if it was not possible to compose these observations with one another. In practice this means enabling zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs to receive other zkSNARK and zkSTARK proofs as inputs, thus allowing to combine arbitrary computations with one another, and use the output of one computation as the input of another, while keeping still compressing all of this computation into a single proof.
Understanding the recursive aspect of zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs means understanding the Verifiable Computation Model enabled by them. An intrinsicate explanation of this powerful mechanism is outside of the scope of this article, but it’s covered in detail in my article on recursive zkSNARKs. I invite everyone eager to master these concepts and the practical mental model of ZKPs to read it.
Private Data As A First-Class Citizen
In the realm of Web3, privcy is of paramount importance. Web 3 is not about taking over the existing Web 2 solutions of today, but rather about building the solutions of tomorrow. Internet was never built for privacy, and in most existing products privacy is treated as a feature, and often implemented as an afterthought. A big misconception is that blockchains are all about privacy, but in reality, they are all about transparency, integrity and authenticity. In fact, the applications on blockchains like Ethereum are more private than “traditional” applications, not due to the blockchain techology itself, but due to the hyper-public nature of all of the data that you store on it. Given that every piece of information that you submit to the blockchain is public, and the fact the blockchain acts as a “global database”, building an application in a manner that is not private by design is almost a guarantee of use of that information for malicious purpuses, often with a moentary or privacy cost to the user.
This requirement for public data is a inherent requrement of the Verifiable Computational Model employed by the EVM. Since the whole computation has to be re-run verbatim by the consensus protocol participants, those participants must have access to all of the data that was used in the computation. Verifiable computation protocols engineered using ZKPs, like zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs have the concept of private inputs and public inputs. Both serve as intputs (arguments) to the computation, but while the public inputs are shared with the verifiers, the private inputs are kept private to the prover. The verifier only needs to have access to the public inputs, not the private inputs, in order to verify the correctness of the computation. We can think of the Verifiable Computation Model of EVM as one where all of the inputs to the computation are public. These aspects are covered in depth in my article on zkSNARKs.
Private Data On The EVM
As discussed earlier, the EVM does not support private inputs to the computation. If an application on the EVM requires private data, they usually achieve this by deploying zkSNARK verifiers as a smart contract on the blockchain. This is what tools like ZoKrates do. This is also the manner by which Polygon Hermez L2 rolls-ups (compresses) transactions into a single proof, and then submits that proof to the Ethereum L1 blockchain.
While it is possible to use zkSNARKs on the EVM, it is impractical to do so, as you are severely limited by the gas fees and the instruction limits. This is where zkSNARK-native blockchains like Mina Protocol disrupt with their value proposition.
It Ain’t Nothin But A Polynomial Thang
Do not get anxious if it takes you some time to gasp the concepts covered here fully. Having built zkLocus - a first of its kind solution for authenticated, private and programmable geolocation sharing off & on-chain, I can tell you from the first-hand experience, that as long as you continiously learn and challenge your own ideas, you will eventually contruct the mental model which will enable you to engineer disruptive solutions while you’re taking a shower.
Zero-Knowledge based computation is very distinct from the programming languages modelled on the von Neumann architecture. When you are programming in languages like Solidity, JavaScript, Python, Java or Scala, you are essentially instructing your computer to store data in registers and perform mathematical operations on that data. You have constructs like if statements, which allow you to branch the execution based on the value of a variable, and loops, which allow you to repeat a block of code multiple times. In Zero-Knowledge proofs, there is no such thing as branching logic or loops. Instead, the computation is represented as a polynomial, and the proof is generated by evaluating that polynomial at a specific point. The verifier then checks that the polynomial was evaluated correctly, and that the result is consistent with the inputs and outputs of the computation.At the core of this difference is the fact that Zero-Knowledge Proofs are just polynomials.
What Is A Polynomial? Is It The Same As An Equation?
It’s important to not only understand what are polynomials, but also understand how they differ from mathematical equations. You likely immersed into equations in high school maths (if you learned them on your own, big props to you!!), but in this context it’s likely that you learned how to solve them without thinking too deeply about it.
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. For example, 3x + 2 = 8 is an equation, where 3x + 2 is one expression, and 8 is another expression. The goal is to find the value of x that makes the equation true. In contrast, a polynomial is a mathematical expression that consists of variables, coefficients, and exponents. For example, 3x^2 + 2x + 1 is a polynomial, where x is the variable, 3, 2, and 1 are the coefficients, and 2, 1, and 0 are the exponents. The polynomial is evaluated by substituting a value for the variable, and then performing the mathematical operations. For example, if we substitute x = 2 into the polynomial 3x^2 + 2x + 1, we get 3 * 2^2 + 2 * 2 + 1 = 3 * 4 + 2 * 2 + 1 = 12 + 4 + 1 = 17.
In the context of Zero-Knowledge proofs, computations are represented as systems of polynomial equations, which are sets of polynomial equations that are solved together. These systems are deterministic and do not have the concept of traditional control flow like loops or conditional branches. Instead, all possible paths of execution are computed, and the correct result is selected based on the inputs.
Control Flow In Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Loops & Conditional Branches
As mentioned previously, Zero-Knowledge circuits are deterministic, which means that branching and dynamic structures and loops are not possible. Does that mean that you can’t have conditional logic or loops in Zero-Knowledge proofs? Not exactly. You can mimic the behavior of conditional logic and loops in Zero-Knowledge proofs, but the structure of the circuit has to be fixed:
-
For conditional logic, you can’t just execute one branch of the computation based on a condition. Instead, you have to compute both branches and then use the condition to select the correct result. This is often done using a multiplexer, a circuit element that takes a condition and two inputs, and outputs the value of one of the inputs based on the condition.
-
For loops, you can’t have a variable number of iterations, because the circuit size has to be fixed. Instead, you have to unroll the loop to a fixed number of iterations. If the maximum number of iterations is not known in advance, you have to set a limit and design the circuit to handle the maximum possible number of iterations.
So, while you can mimic the behavior of loops and conditional branches in Zero-Knowledge proofs, it’s not the same as in traditional programming languages. The computation has to be deterministic and the structure of the circuit has to be fixed. In practice this means that you need to adapt your mental model and design your solution to respect the framework of Zero-Knowledge circuits, rather than trying to fit the Zero-Knowledge circuits into the framework of traditional programming languages. Architecting and designing Zero-Knowledge applications is extremely fun and rewarding. In my personal experience of building a first-of-its kind authenticated & private geolocation protocol zkLocus, I have found that I always manage to address every technical challenge that I faced, and that I always come out of it with a better understanding of the technology and a more refined mental model of how to engineer solutions on top of it. Do not let the initial friction that you may face to discourage you.
Combining zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs With The Blockchain

Blockchains excel as an authenticated, transparent, distributed, fault-tolerant and integirty-assured state machine and data storage layer. Changes to on-chain data are performed during state transitions, and state transitions are encoded in transactions. zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs excel at representing verifiable computation. You can combine both in a way where each blockchain transaction is represented by a zkSNARK or zkSTARK proof. In the case of a smart contract execution, this proof contains the proof of the observation of the execution of the smart contract’s code, alongside any changes to the on-chain state resulting from the execution of that smart contract. In such an architecture, zkSNARK/zkSTARK proofs represent the execution layer, and the blockchain the data storage layer. The client submitting the transactions are the prover, and the blockchain is the verifier.
The previous paragraph encompasses the core idea of how blockchains leveraging the Verifiable Computation Model enabled by zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs operate. It also provides an intuition on how Zero-Knowledge Applications (zkApps) built on top of those architectures operate. But let’s not just leave it at the intuition level. Developing a solid understanding of these concepts will enable you to construct a mental model which you can apply to novel scenarios, and engineer disruptive solutions. With this in mind, we will now explore how zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs are used in the Mina Protocol and Polygon Maiden blockchains, as well as analyze how zkLocus is using Mina and zkSNARKs to turn geolocation data into a Real World Asset (RWA) on-chain, and enable private, verifiable and programmable geolocation sharing.
The Mina Protocol Blockchain
The Mina Protocol blockchain works, by combining zkSNARKs with the Ouroboros Samasika consensus protocol. When developing applications/smart contracts on Mina, you are writing zkSNARKs circuits designed to represent an observation of a computation. You can think of Mina, as “low-level” zkSNARKs blockchain, where you are directly interacting with zkSNARKs circuits. This gives Mina the unique value proposition of flexibility and portability. By exposing and allowing to operate on and compose raw zkSNARKs proofs, it allows to you to freely use those constructs without an opinianated abstraction on top. Given that Mina operates on raw zkSNARKs, it means that those zkSNARKs can be used and integrated with systems outside of Mina. This is how zkLocus operates natively on the Mina blockchain, but can also be used with other blockchains, or even in an off-chain environment, such as as with Web 2. Refer to the article introducing zkLocus for more information.
In Mina, you write zkSNARKs in JavaScript/TypeScript, by using the O1JS framework, which acts as a Domain Specific Language (DSL). O1JS is based on SnarkJS, which is the lower-level implementaion of zkSNARKs in JavaScript. You encode the Zero-Knowledge and their constraints using the basic constructs provided by O1JS, which later get compiled down to zkSNARKs. Those zkSNARKs can then be either used directly on the Mina blockchain, or exported and used in other environments, including off-chain. You can find a practical guide on how easy it is to write zkSNARKs in O1JS in my article covering zkSNARKs.
If you are keen on being up to date with the latest developments and projects on Mina, comMINAty is a great Twitter/X acccount to follow. It’s lead by the same team behind zkok.io, where zkLocus is also listed.
zkLocus + Mina Protocol
zkLocus is an application, a framework and a protocol, which leverages zkSNARKs to turn geolocation data into a Real World Asset (RWA) on-chain, and enable private, verifiable and programmable geolocation sharing. zkLocus is implemented natively on the Mina blockchain, and this is where we are developing $ZKL token - the native token of the zkLocus protocol, alongside its utility use-cases. At the same time, it’s possible to use zkLocus with other blockchains, or even in an off-chain environment, such as with traditional Web 2 applications. At the core of the architecture of zkLocus there are two main components:
-
The raw zkSNARKs circuits (known as
ZkPrograms in O1JS), on top of which zkLocus builds its application chain and execution logic. These zkSNARKs circuits are compatible with the Mina blockchain, but they can also be used independently, with other blockchains, or even in an off-chain environment. The zkSNARKs circuits are designed to represent the observation of a computation, alongside all of its inputs and outputs. The zkSNARKs circuits are written in JavaScript/TypeScript, using the O1JS framework, which acts as a Domain Specific Language (DSL) for zkSNARKs. The output of the execution of these zkSNARKs circuits is a zkSNARK proof, which can then be verified by anyone and have its public outputs extracted. -
The smart contracts that are deployed on the Mina blockchain and serve as an interface between the raw zkSNARKs application chain of zkLocus and the Mina blockchain. These smart contracts are also written in JavaScript/TypeScript, using the O1JS framework, and it’s trivial to integrate the raw zkSNARK proofs with them. Under the hood, the smart contracts are abstractions on top of the same
ZkProgramprimitives, adapted to be compatible with the execution layer offered by the Mina protocol.
Given the goal of offering geolocation as a Real World Asset (RWA) on-chain, while maintaining flexibility and portability, zkLocus found its perfect match with Mina 💜. While it’s indeed possible to verify zkLocus proofs direcly in languages like JavaScript, TypeScript and Rust, as well as verify and use zkLocus proofs on other blockchains like Ethereum, the easiest way of integrating zkLocus with other blockchain technologies could be through bridging. The reality is that verifying complex zkSNARK proofs on blockchains like Ethereum will probably cross the gas limits, while also presenting challenges for their direct integration.
The Polygon Maiden Blockchain
Polygon Maiden is another blockchain that uses Zero-Knowledge Proofs at the execution layer, by leveraging zkSTARKs to build a zkEVM with familiar x86 assembly-like instructions. When writing smart contracts on Polygon Maiden, you are not interacting with zkSTARKs directly, but instead writing assembly-like instructions which operate as a virtual machine. The execution of that virtual machine is “cryptographically observed” by zkSTARKs. Such virtual machine constructs are referred to as a zero-knowledge virtual machine (zkVM).
The smart contract code that you write on Polygon Maiden would be similar to the one that you would write in languages like Solidity, Python and JavaScript. The Polygon Maiden VM is turing-complete, and exposes you to the familiar flow control constructs like if statements and loops. The Polygon Maiden’s VM can be thought of as a foundational layer, similar to WebAssembly (WASM). It’s designed to provide a basic set of instructions that can be further abstracted. Just as WASM allows high-level languages like JavaScript to be compiled down to it, the Polygon Maiden’s VM is designed to support higher-level languages. This design enables developers to write code in familiar languages, which can then be compiled down to run on the Polygon Maiden’s VM. The execution of a transaction involves a coordinated interaction between various components of the protocol.
What Is A Computer Program?
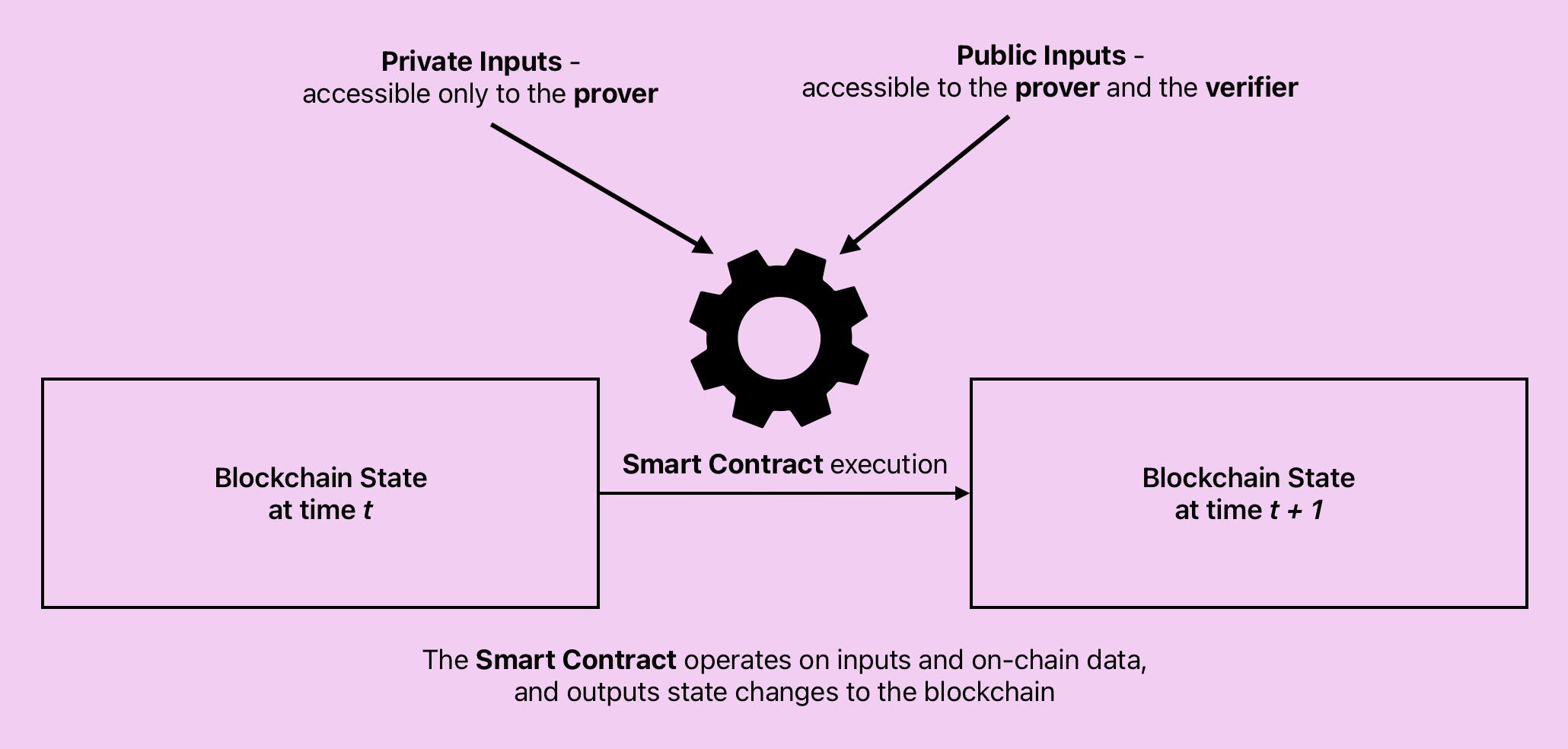
In order to build an ever deeper understanding of how blockchains with execution layer based on Zero-Knowledge Proof constructs like zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs operate, let’s analyze what a computer program is. At a more abstract level, a computer program is a set of instructions that a computer executes, while following a stric set of rules. Several computer programs can be composed together to form an even more abstract entity, which materializes itself as a product that solves a problem, by addressing a need. This level of thinking is extermely valuable when architecting solutions, but it may not be sufficient to fully gasp the intricacies of zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs.
At a more concrete level, a computer program is composed of the following 3 components:
- The set of instructions to be executed.
- The inputs (arguments) to the computation.
- The outputs (results) of the computation.
In order to construct a Verifiable Computation Model, it is necessary to cryptographically “observe” the execution of the computer program, alongside all of its inputs and outputs. As such, it’s not sufficient to merely provide a proof of the correct exeuction of the instructions, but also that that execution was performed on specific inputs, and that the outputs are consistent with the inputs and the execution of the instructions. This is precisely how zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs operate. They provide a cryptographic observation of the computation, alongside all of its inputs and outputs. Verifying the Zero-Knowledge Proof of a program execution, means also verifying the correctness of the inputs and outputs of that computation, as they are all cryptographically linked with one another in the proof. In other words, to generate zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs proof of an “observation of a computation” means to produce a cryptographic proof that a specific set of instructions (computer program/zero-knowledge circuit/smart contract) were executed, and that those instructions were executed on specific inputs, and that the outputs of that computation are consistent with the inputs and the execution of the instructions. Changing any of the inputs, outputs or the instructions would result in an invalid proof.
zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs: Addressing The Limitations Of The EVM’s VCM

Now that we’re equiped with a mental model of the means by which zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs operate, we are ready to understand how their unique properties address the limitations of the EVM’s Verifiable Computation Model.
Arbitrary Complexity
The EVM’s Verifiable Computation Model is limited by the gas fees and the instruction limits. This makes it impossible to execute complex programs on the EVM. In contrast, zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs enable a novel verifiable computation model that is infinitely scalable and constant in time, cost, and size. This means that you can execute complex algorithms on zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs, without being limited by the gas fees and the instruction limits. For example, you can run a complex algorithm for several hours or days and submit the result of that execution to the blockchain. Examples of such algorithms include machine learning models, simulations, predictions, and games.
This is enabled by the fact that verifying a zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs proof takes approximately constant time, cost, and size, regardless of the complexity of the underlying computation. This is in contrast to the EVM, where the verification of a smart contract execution takes time, cost, and size proportional to the complexity of the smart contract. In the section that follows we will explore how this allows us to further refine the definition of our Verifiable Computation Model.
Infinite Scalability
zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs provide a unique value proposition of infinite scalability. This is enabled by the recursive nature of zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs, which allows for a zkSNARK/zkSTARK circuit to receive other zkSNARK/zkSTARK proofs as inputs, and then use the outputs of that computation within its logic. This allows for the composition of arbitrary computations, and the compression of all of those computations into a single proof. This is in contrast to the EVM, where the computation is re-executed by all validators, and the scalability is limited by the redundancy of the execution. In practice, this means that you can grab 1000 individual proofs, and compress them all together into a single proof. That single proof (not referring to its marital status, but rather numeric quantity) contains cryptographic observation of the computation of all of those 1000 individual proofs, alongside all of their inputs and outputs. The time to verify that single proof is approximately the same as the time to verify a single proof. This is the essence of infinite scalability.
Layer 2 (L2) Solutions On Ethereum (Validiums)
You can now understand why most Layer 2 (L2) solutions on Ethereum are built using zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs. They allow for the compression of multiple transactions into a single proof, which can then be submitted to the Ethereum blockchain. This is how solutions like Polygon Hermez L2 roll-ups work. They process the transactions performing computations on their own side-chain, and then produce compress multiple transactions into a single proof, and then submit that proof to the Ethereum L1 blockchain. In such a setup, the Ethereum L1 blockchain acts as a verifier, and the L2 side-chains acts as a prover. Ethereum L1 becomes a verifier by having a smart contract that can verify the proof, and the L2 side-chain becomes a prover by generating the proof of the observation of the computation. L2’s that operate in this manner are known as validiums, since they validate the correct execution of the transactions and state changes on their side-chain, and then store a cryptographic commitment to that execution on the Ethereum L1 blockchain. Such approaches at scaling Ethereum, known as roll-ups, have been so successful that their ideas have been included into the roadmap of Ethereum.
zkLocus As A Mina Roll-Up
Following the perspective of infinite scalability, zkLocus can be seen as a roll-up on Mina. By having all of the computation performed off-chain, and then integrating those computations with one another and compressing them into a single proof, zkLocus effectively uses Mina for settlement and storage. Once a geolocation proof is verified on Mina, it is stored on the blockchain, thus enabling the geolocation data to be used as a Real World Asset (RWA) on-chain. Since zkLocus focuses on rolling-up/compressing/combining computations pretinent to its own logic (everything related to its functionality and features), it’s called an application-specific roll-up/application chain (app chain). This is in contrast to general-purpose roll-ups, which aim to compress all of the transactions on a blockchain into a single proof.
Energy Efficiency
Given the features of proof verification being approximately constant in time, cost, and size, regardless of the complexity of the underlying computation, as well as the ability to compress multiple proofs into a single proof, zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs are energy efficient. This is in contrast to the EVM, where the computation is re-executed by all validators, and the energy cost of the computation is proportional to the number of validators and computational steps (smart contract instructions). In practice, this means that the energy cost of verifying a zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs proof is approximately the same, regardless of the complexity of the underlying computation. This is a significant advantage, as it allows for the execution of complex algorithms on zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs, without incurring a significant energy cost.
Privacy
As discussed earlier, the EVM’s Verifiable Computation Model is limited by the requirement that all of the inputs to the computation are public. zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs proofs represent a cryptographic observation of the computation and support two types of inputs:
- Public inputs - these are inputs to the computation that are used when generating the proofs, and are shared with the verifier(s). The verifier(s) then use these inputs to verify the correctness of the computation. As such, public inputs are used to generate the proof, and then to verify that same proof.
- Private inputs - these are inputs to the computation that are used to generate the proofs, but are not shared with the verifier(s). The verifier(s) do not need to know the private inputs in order to verify the correctness of the computation. Private inputs remain known only to the prover, but not the verifier. In other words, these are arguments to the computation that are kept private to the prover (client), and are not shared with the verifier (blockchain/consensus participants). A private input to a computation is also referred to as a witness.
The support for private arguments/inputs offers a significant advantage, as it allows for the execution of computations on private data, such as personal information, financial information, and encryption keys. This is in contrast to the EVM, where the computation is performed on public data, and all of the inputs, outputs, and intermediate states are publicly visible.
Secret Values On Ethereum
While it is technically possible to have private inputs/secret values on Ethereum, it is impractical and comes with limitations. The way you achieve it is by deploying zkSNARK verifiers as smart contracts on the blockchain. This is what tools like ZoKrates do. The impracticality and limitations come from the fact that you are severely limited by the gas fees and the instruction limits. Zero-Knowledge Proofs are polynomials and mathematical operations on those polynomials. Verifying a proof takes a lot of computational steps. The EVM execution model’s scope falls outside of these applications. This is where zkSNARK-native blockchains like Mina Protocol disrupt with their value proposition.
zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs: Beyond Blockchain

zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs are frequently used in the context of blockchains, but they do not have to be. Given the information we’ve covered so far in this article, the statement that zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs can exist outside the realm of blockchains should not come as a surprise. This is, however, something very important to understand, even at the risk of over-repeating it. The Verifiable Computational Model enabled by zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs is independent of the blockchain technology, in fact, most of the Zero-Knowledge mathematics predate the blockchain technology. Although it was the developments in the blockchain space that propelled the interest in ZKP at an exponential rate. As such, the blockchain is simply an environment where these Zero-Knowledge protocols flourish. Think about it this way: if we would like to prove computations to one another we would end up to have to share these computations with one another, alongside all of the shared state. To address this, we would end up creating something like the blockchain.
zkLocus: Off-Chain Geolocation Sharing
As already mentioned, zkLocus can operate completely off-chain. In fact, the core Zero-Knowledge circuits of zkLocus are designed as fully independent observations of the computations, and thus can be operated on directly, without ever interacting with a blockchain. One of our ongoing integrations involves generating and verifying zkLocus proofs off-chain, and then bridging part of that data on-chain, while using other for subsequent off-chain computations.
Time Complexity of EVM vs zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs

Before we conclude, and now that we are equipped with a practical understanding of the novel Verifiable Computational model enabled by zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs, we will connect the concepts covered in this article to reason and compare the time complexity of the VCM of the EVM and zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs. In this process, we will further expand on the definition of VCM to clearly distinguish the two models.
The discussion in this section will not be overlly technical, with the focus being not on absolute mathematical precision, but rather on providing a well-reasoned approximation, which you will find very useful when reasoning and comparing the solutions.
Time Complexity of Executing The Computation
The time complexity of executing the computation is generally smaller in the EVM than in zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs. This is because in the EVM executing
the computation is simply emulating the virtual machine instructions of the EVM. Here, we have familiar constructs like stack, memory, storage and control flow. The time complexity of executing the computation in the EVM is linearly proportional to the number of instructions executed by the smart contract, so we can roughly approximate it to O(n), where n is the number of instructions executed by the smart contract.
In zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs, computations are represented as a set of arithmetic constraints. The complexity is often proportional to the number of these constraints because the prover needs to generate a proof that these constraints hold. Therefore, in such systems, n' can be considered as the number of constraints. For zkSNARKs, the time complexity of generating the proof would be O(n'). For zkSTARKs, the time complexity of generating the proof would be O(log(n')).
It’s important to note that the time complexity of producing the proofs also depends on the size of the computation/input, which includes public inputs and any private data used in the computation. As mentioned at the start of this section, we focus on practicality in lieu of detailed mathematical precision.
In practice, the time complexity of executing/proving the computation in EVM is generally smaller than in zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs. In other words, the client-side execution of the computation is faster in the EVM than in zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs. There is no direct mapping between the number of contraints that you would need to represet a particular EVM computation in zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs, and n != n'.
Time Complexity of Verifying The Computation
In the EVM the process of verifying a computation is symmetrical, i.e. the same, to the process of executing that computation: in both cases the computation must be (re)executed verbatim. In ZK protocols of zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs, these processes are asymmetrical, i.e. different. The time complexity of verifying the correctness of a claimed computation is where zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs disrupt with their value proposition, by addressing the issue of scalability. In the context of blockchain, the computations are submitted via transactions. We say that a computation is claimed, when it has been submitted onto the blockchain (the mempool), but has not yet been verified by the consensus participants, i.e. that transaction has not yet been included in a block. The participants of the consensus protocol are the verifiers of the computation. In the EVM, the verifiers have to re-execute the computation, while in zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs, the verifiers only need to verify the proof.
The time complexity of verifying a claimed computation on the EVM is drectly proportional to the number of instructions in the smart contract being executed (n), multiplied by the number of validators (v) that participate in the consensus. As such, the time complexity of verifying a claimed computation on the EVM is O(n * v). This is because these validators have to re-execute the smart contract on their own machines.
In contrast, the time complexity of verifying a claimed zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs computation is approximately constant, regardless of the complexity of the underlying computation, and as such we define this complexity to be of O(1). To be more precise, each participating validator takes a constant time to verify any computation. If v' is the number of the validators participating in the consensus, then the time complexity of verifying a claimed zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs computation is O(v'). This is because the verification of the proof is performed in constant time, cost, and size, and does not depend on the complexity of the computation.
When analyzing time complexity, the low-level details are compressed into an expression describes the growth of the computation as a function of the input size. Given that in both of the cases, the number of validators is a constant, the time complexity of verifying a claimed computation on the EVM is directly proportional to the number of instructions in the smart contract being executed, while the time complexity of verifying a claimed zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs computation is constant. As such, we can define the time complexity of verifying a claimed computation on the EVM as O(n), and the time complexity of verifying a claimed zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs computation as O(1).
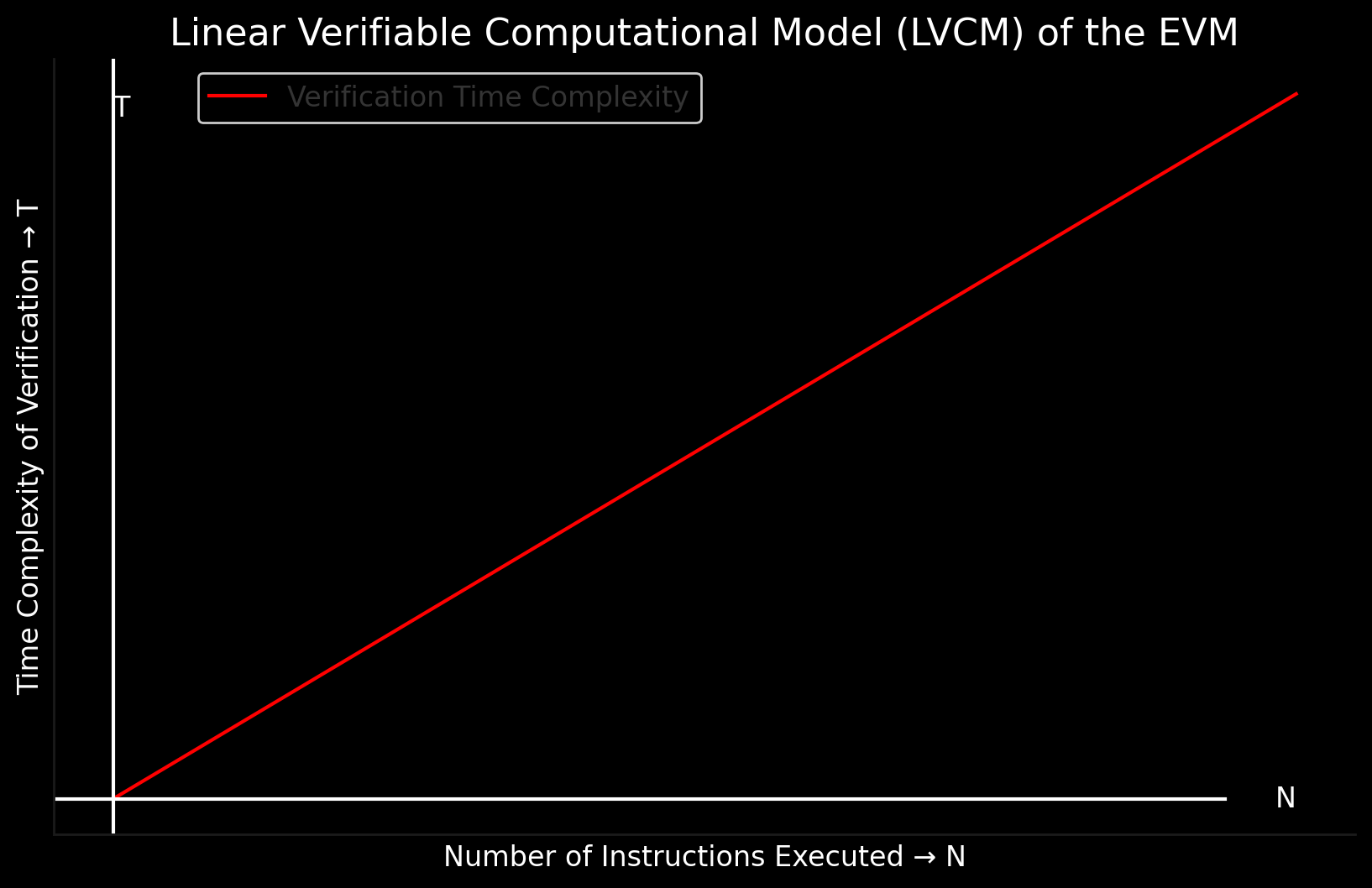
From this, we can futher refine our Verifiable Computational Model (VCM) definition to include the take into consideration the time complexity of verifying the correctness of the claimed computaion. As such, we will call the Verifiable Computational Model of the EVM Linear Verifiable Computational Model (LVCM), and the Verifiable Computational Model of zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs Constant Verifiable Computational Model (CVCM).
Linear Verifiable Computational Model (LVCM) of the EVM
The Linear Verifiable Computational Model (LVCM) of the EVM is defined by the time complexity of verifying the correctness of the claimed computation being directly proportional to the number of instructions in the smart contract being executed. The time complexity of verifying a claimed computation on the EVM is O(n), where n is the number of instructions in the smart contract being executed. We call it linear because the time complexity grows linearly with the number of instructions in the smart contract being executed. It can be visualized as a straight line on a graph, where the x-axis represents the number of instructions in the smart contract being executed, and the y-axis represents the time complexity of verifying the correctness of the claimed computation:
Constant Verifiable Computational Model (CVCM) of zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs
The Constant Verifiable Computational Model (CVCM) of zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs is defined by the time complexity of verifying the correctness of the claimed computation being constant. The time complexity of verifying a claimed zkSNARKs/zkSTARKs computation is O(1), regardless of the complexity of the underlying computation. We call it constant because the time complexity is constant and does not depend on the complexity of the computation. It can be visualized as a horizontal line on a graph, where the x-axis represents the number of constraints in the circuit (equivalent to number of lines of code in the smart contract) whose proof is being verified, and the y-axis represents the time complexity of verifying the correctness of the claimed computation:

zkSafeZones - Blockchain & Zero-Knowledge Proofs For Humanity

In this article I have mentioned several times that Zero-Knowledge proofs combined with public blockchains offer a unique architecture, which is inherently authenticated, trustless, transparent, fault-tolerant, and integrity-assured. We can leverage these technologies to build a better future for humanity and Planet Earth. This is one of our core missions at zkLocus - the geolocation is just a start. Before we conclude, we will briefly examine how zkSafeZones, which is our initiative upon the zkLocus framework, leverages Zero-Knowledge Proofs and blockchain technology to safeguard civilians in conflict zones, and sets the groundwork for the automation of legal compliance on-chain at a global scale.
By leveraging the privacy-preserving and verifiable computation capabilities of Zero-Knowledge Proofs, zkSafeZones enables civilians to securely and anonymously report their locations in war-torn areas, facilitating targeted aid efforts and providing an unprecedented level of transparency and accountability in adhering to international humanitarian law.
Moreover, the integration of smart contract technology with Zero-Knowledge Proofs paves the way for automated enforcement of international agreements, allowing for the creation of self-executing contracts that trigger predefined legal actions based on verified geolocation data. Beyond its immediate application in conflict zones, the framework proposed in zkSafeZones has the potential to transform various domains where geolocation data plays a crucial role, from supply chain management and delivery verification to legal proofs for drone operations. As the international community grapples with the complexities of modern conflicts and the challenges of enforcing humanitarian laws, initiatives like zkSafeZones practically demonstrate how the power of ZKPs and blockchain can be used to solve important issues, by addressing them from a novel perspective.
We are proposing zkSafeZones to the United Nations (UN) and the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), and are actively seeking partnerships with organizations and individuals that share our vision of leveraging technology to create a more transparent, accountable, and humane world. If you are interested in learning more about zkSafeZones or collaborating with us, please reach out to us at contact@zklocus.dev or on Twitter/X @zkLocus.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the novel Verifiable Computation Model enabled by zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs opens up a realm of possibilities that extends far beyond the constraints of the EVM’s model. By shifting the bulk of computation off-chain to the prover of the computation (client) and offering constant time complexity for verifying these proofs of computation on-chain, these Zero-Knowledge Protocols pave the way for infinitely scalable, privacy-preserving applications.
As we’ve seen with zkLocus leveraging Mina’s zkSNARK-based architecture to turn geolocation data into a trustless and programmable Real World Asset (RWA), the potential use cases are vast and disruptive. Yet the power of zkSNARKs and zkSTARKs is not limited to the blockchain context alone. These cryptographic techniques can be applied anywhere there’s a need for verifiable computation and private inputs. For example, we can build AI survaillance systems that fully respect privacy, and work on this is already being done in the field of Zero-Knowledge Machile Learning (zkML).
zkSafeZones is a practical example of how we can combine Zero-Knowledge Proof protocols with the blockchain to solve important problems that still remain unaddressed by existing technology. By leveraging these approaches in the realm of geolocation, as exemplified by zkLocus, we open up a transformative potential in tackling humanitarian challenges and automating the enforcement of international law. Just like how zkLocus turns geolocation into a programmable and trustless Real World Asset (RWA), zkSafeZones demonstrates how we can harness the power of ZKPs and blockchains to safeguard civilians in conflict zones and create a more transparent, accountable, and humane world.
But it doesn’t stop there. The integration of smart contract technology with ZKPs paves the way for automated enforcement of international agreements, allowing for the creation of self-executing contracts that trigger predefined legal actions based on verified data, starting with geolocation. This is an important step towards automating the enforcement of the law on-chain, and it’s just the beginning. Our practical solution, which we are also proposing to the UN and the ICRC, is a testament to how we can harness these technologies to tackle critical global issues and create a better future for everybody.
Diving into Zero-Knowledge Proofs requires adapting to a new mindset and working within the constraints of the polynomial model rather than traditional control flow. But as my experience building zkLocus has shown, every fricition that you face will be met with a solution, and every solution will deepen your understanding of the technology. Before you know it, you’ll be engineering disruptive solutions while you’re out on a walk, a drive or taking a shower.
So whether you’re aiming to build atop a zkSNARK-powered blockchain like Mina, leverage zkSTARKs for scalable Layer 2 constructs, or utilize Zero-Knowledge Proofs in an off-chain context, embrace the journey of learning. The mental models you construct will serve as a foundation for leveraging these technologies to build a digital future where trust, privacy, scalability and interoperability are not features, but inherent properties of our solutions.
✨ zkLocus: Geolocation Real World Asset (RWA) For Web 3 ✨

Thank you for taking your time to read this article. I sincerely hope that you found it informative and that it has sparked your curiosity about Zero-Knowledge Proofs and their applications. If you have any questions, feedback, or would like to collaborate, please reach out to me at hello@illya.sh, or on Twitter/X @illyaGera.
For more information about zkLocus, you visit one of the following links:
- zklocus.dev - The official homepage of zkLocus. Here you can find the latest updates about zkLocus and contact information.
- GitHub/zkLocus - The GitHub repository of zkLocus. Here you can find the source code of zkLocus.
- x.com/zkLocus - The Twitter/X account of zkLocus. Here you can find the latest updates about zkLocus.
- zkLocus Whitepaper - The whitepaper of zkLocus. Here you can find a detailed description of zkLocus and its underlying technology.
- zkSafeZones Whitepaper - The whitepaper of zkSafeZones. Here you can find the whitepaper for our intiative aiming at safeguarding civilians in conflict zones, and sets the groundwork for enforcement of the law on-chain.
- contact@zklocus.dev - The email address of zkLocus. Here you can directly contact the zkLocus team.
Discuss 🗣️
Currently, the blog does not natively support comments. In the meanwhile, you can discuss this blog post on:
- Twitter/X - 🚀 zkSNARKs & zkSTARKs: A Novel Verifiable Computation Model 🚀
- Reach out to me on Telegram at t.me/illya_gerasymchuk, or e-mail me at hello@illya.sh