CBDC design, pilots & policy updates
Ongoing coverage of retail and wholesale CBDC pilots, architecture choices, legal frameworks and implementation timelines.
governments are already converting from physical currencies to digital currencies
and it makes sense - it's cheaper, more traceable and more controllable. digital currencies are programmable - purely physical are not
i wrote a thread about how virtually central banks are moving to digital currencies - via retail & wholesale CBDCs:
https://illya.sh/threads/@1756336264-1.html
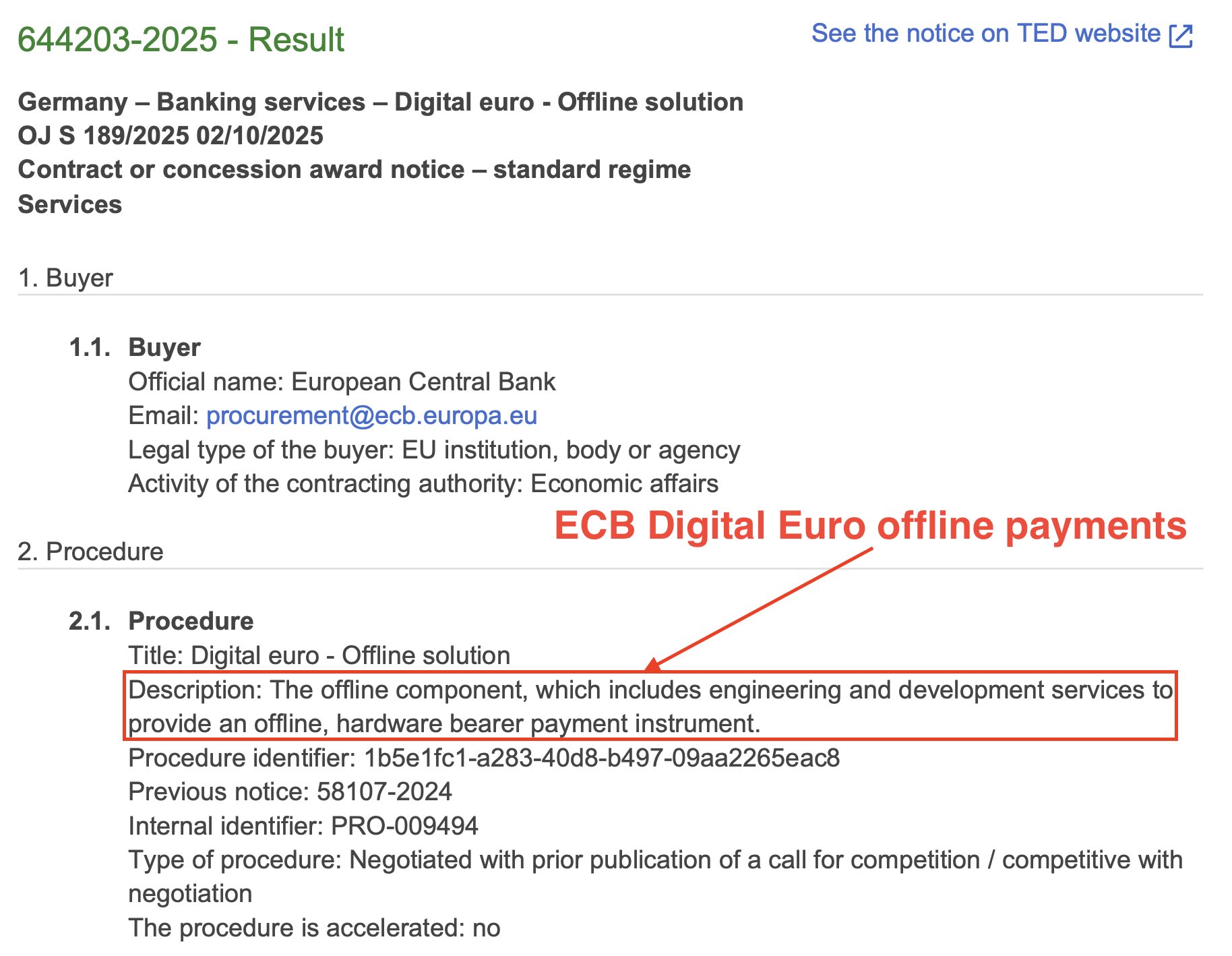
decentralized digital Euro will not work, because the ECB needs to have full control over it
retail CBDCs are direct central bank liabilities on the balance sheet. so "neutral market infrastructure" would not work, because the ECB needs to have full control over it. you can also imagine how many regulations need to be accounted for by the implementation
it most likely won't use a public blockchain for base implementation, and it's definitely not like stablecoins 😄
digital euro also needs to support offline payments, which isn't currently widely supported in DeFi. Zero Knowledge Proofs enable some potential solutions for this, but I don't believe that that's with what the ECB is going with now
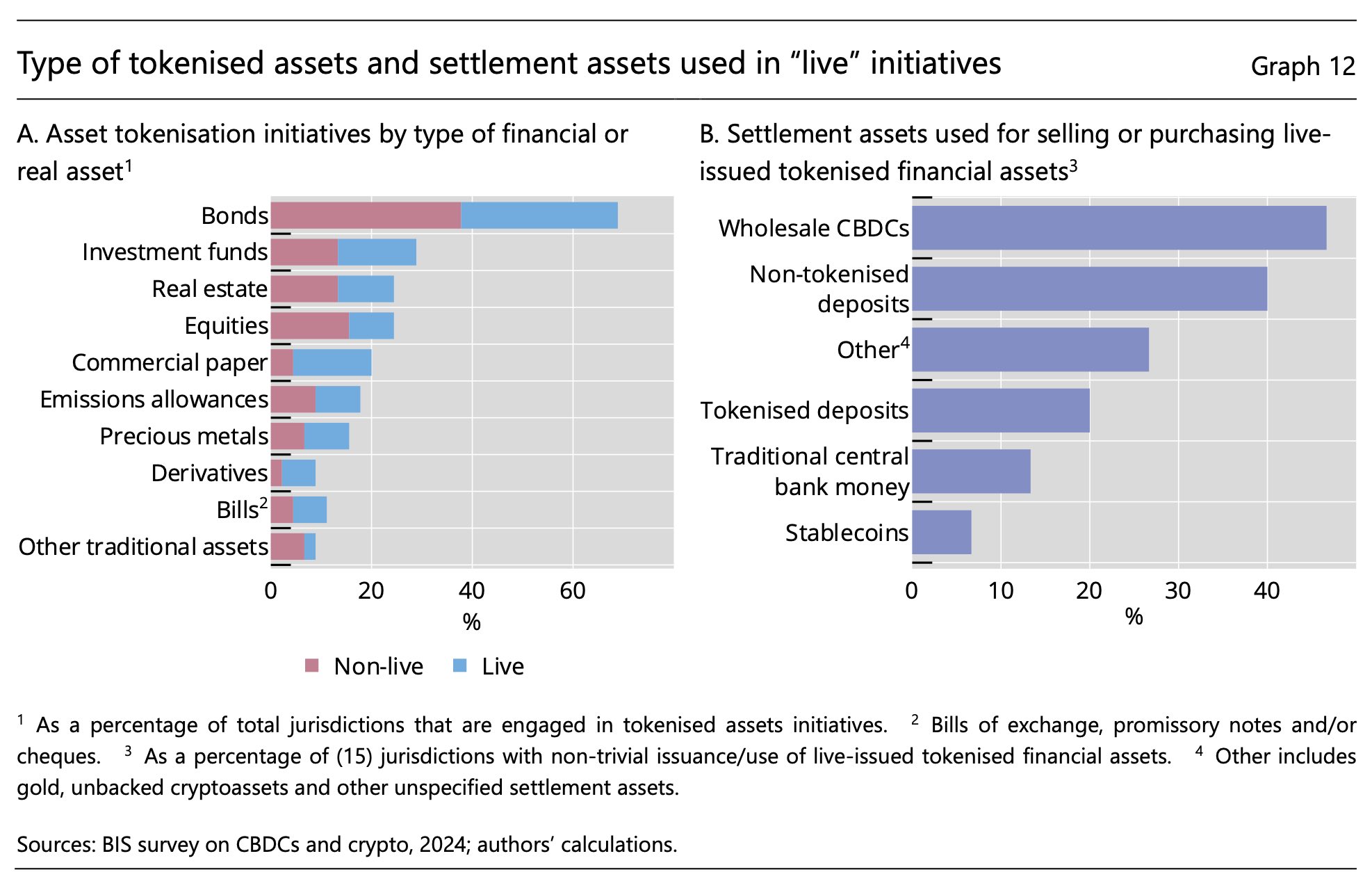
real world and financial asset tokenization is ongoing worldwide, with transactions mostly settled in CBDCs
government and corporate bonds are the most common RWA to be tokenized
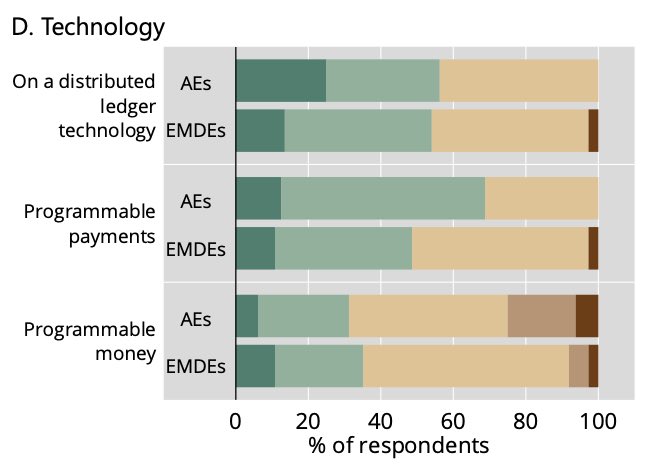
>80% of central banks plan to operate the DLT/blockchain for wholesale CBDCs themselves, hinting an in-house blockchain solution, and not a public and permissionless ledger

however, even if CBDCs are implemented using blockchain - it's unlikely to be a public, permissionless blockchain like Ethereum
however, even if CBDCs are implemented using blockchain - it's unlikely to be a public, permissionless blockchain like Ethereum
>50% of central banks in both, advanced and emerging economies are considering using DLT for wholesale CBDCs
this means that wholesale CBDC is likely to be implemented using some form of blockchain technology - much more likely than the retail CBDC
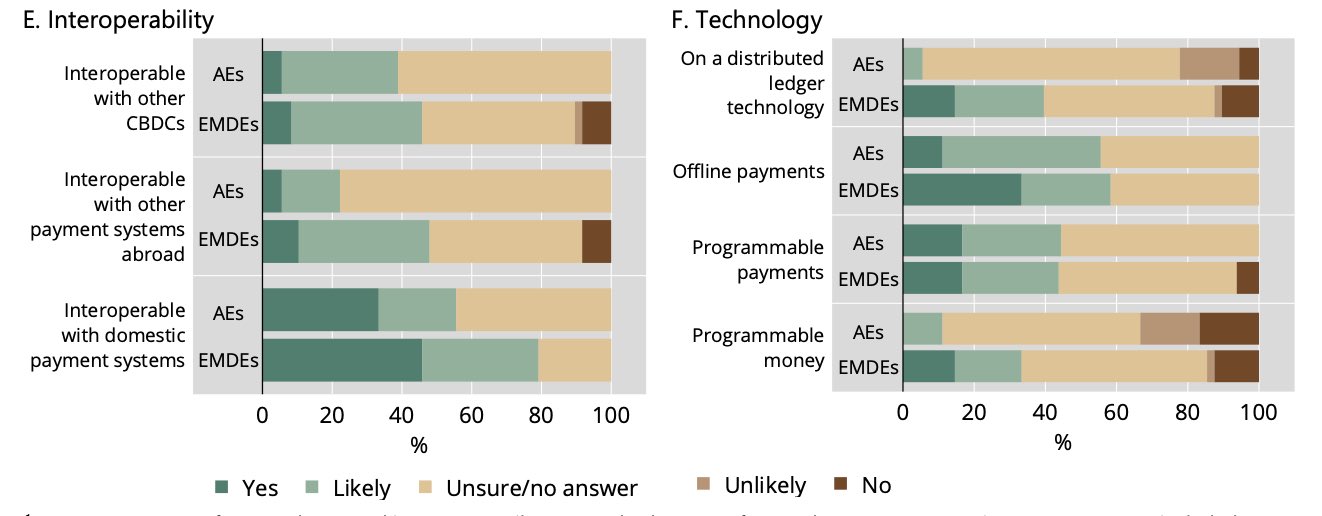
only 6% of advanced economies (AE) central banks and 40% of emerging economies (EM) central banks are considering distributed ledger technology (DLT) as an implementation layer for retail CBDCs
here, consider DLT = blockchain
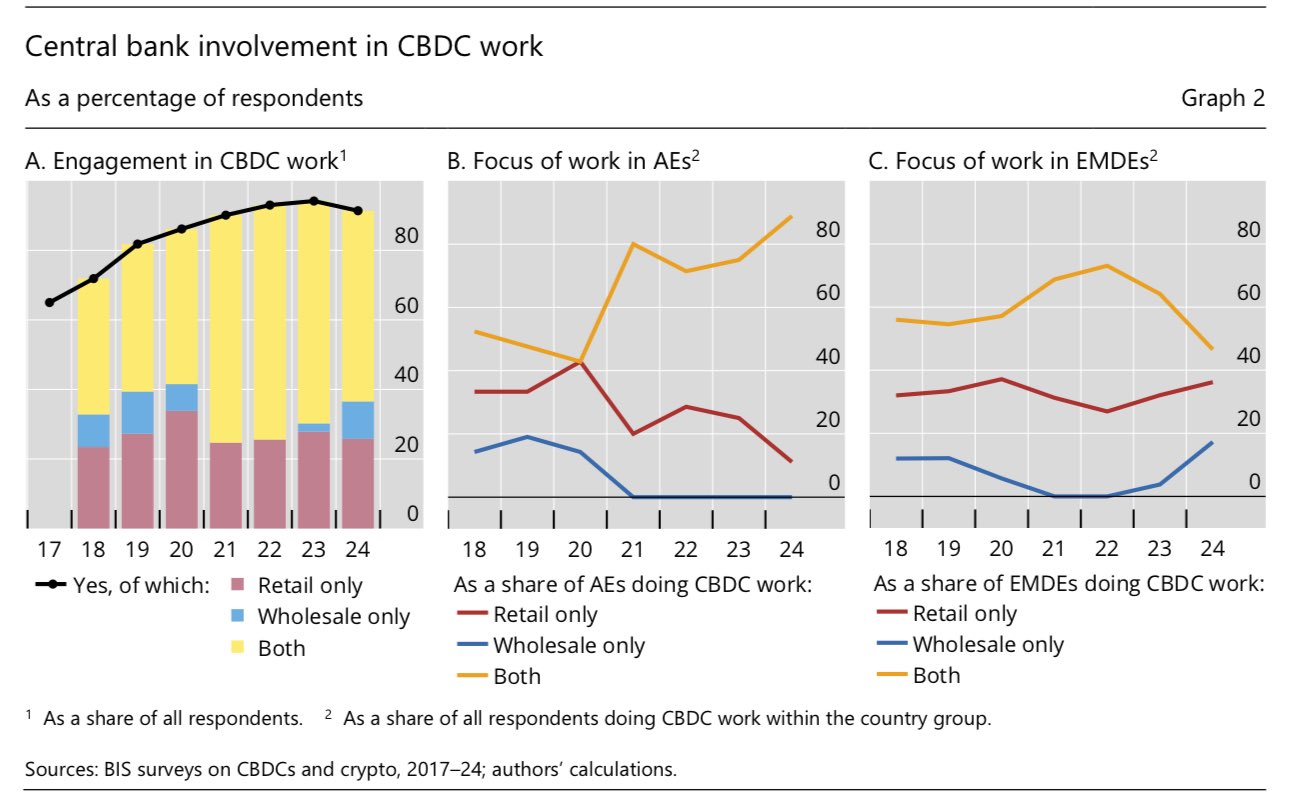
91% of central banks are working on CBDCs, but not on a public blockchain
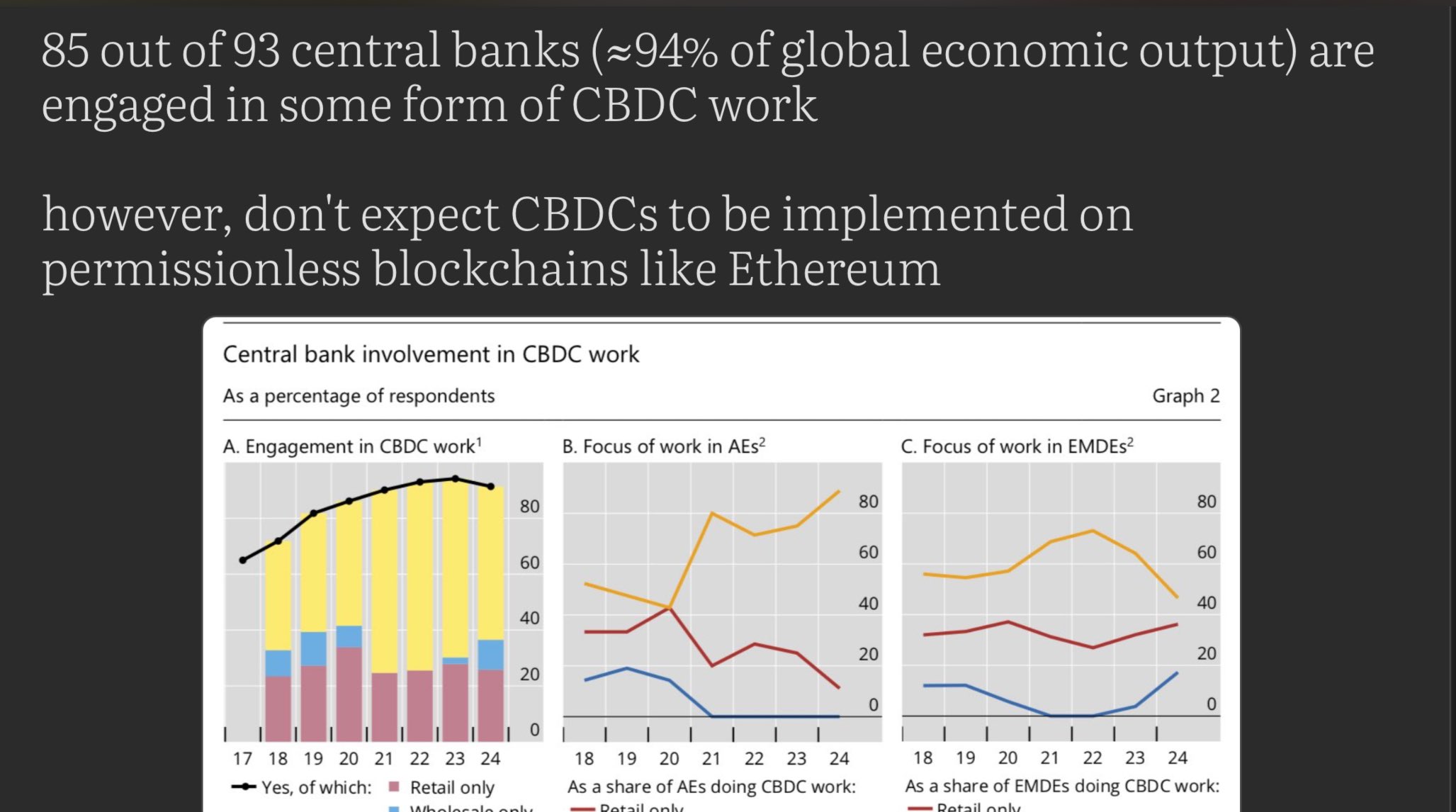
85 out of 93 central banks (≈94% of global economic output) are engaged in some form of CBDC work
however, don't expect CBDCs to be implemented on permissionless blockchains like Ethereum
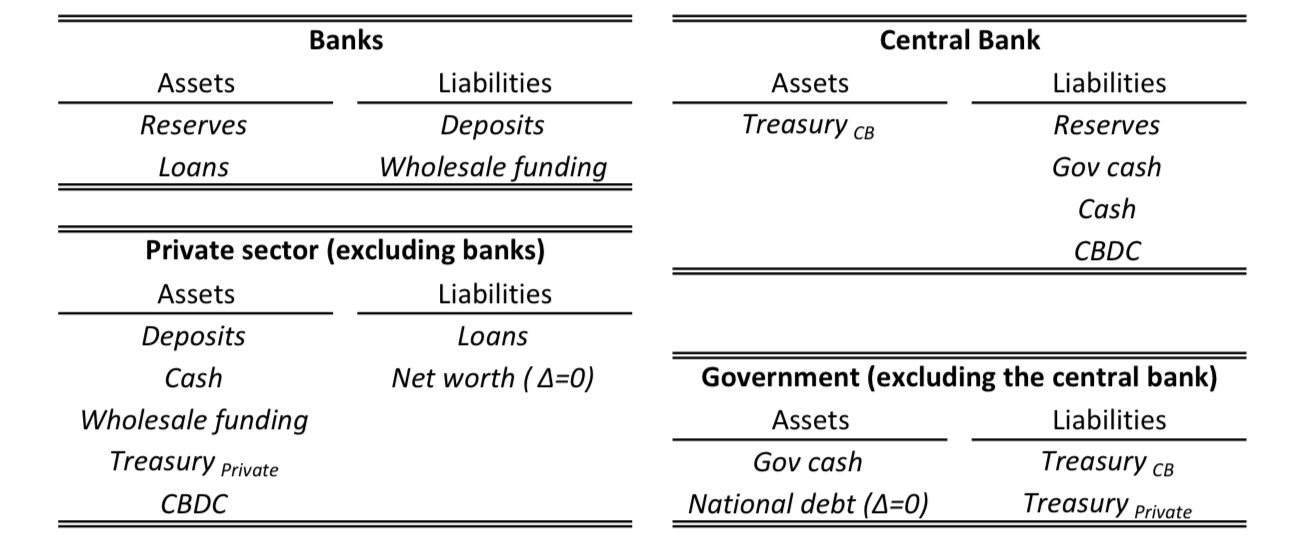
thus, wholesale CBDC is a tokenized/digital version of central bank reserves used by the financial market infrastructure (FMI) and banks
it also lives on the liability side of the central bank

wholesale CBDC will be used by financial institutions only, such as commercial and central banks for interbank and market settlement
wholesale CBDC will only be transacted between select financial institutions - it's not something you'd use as a regular business or consumer
wholesale CBDC will be used by financial institutions only, such as commercial and central banks for interbank and market settlement
wholesale CBDC will only be transacted between select financial institutions - it's not something you'd use as a regular business or consumer
retail CBDC is the digital version of currency - a liability of the central bank in the balance sheet

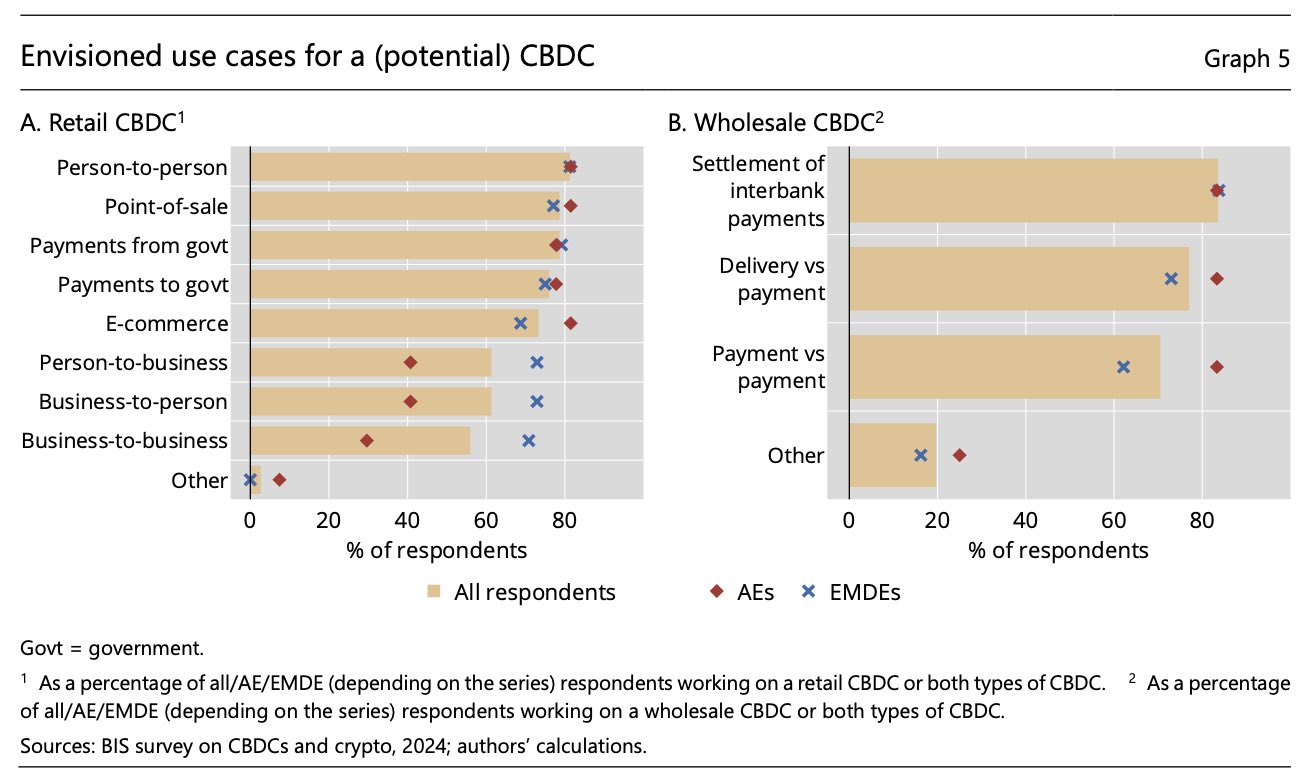
retail CBDC will be used for day-to-day payments, similar to the ones you do with with a credit card. this is the type of CBDC you can use for business and consumer transactions, such as paying for a supermarket purchase
retail CBDC will be used for day-to-day payments, similar to the ones you do with with a credit card. this is the type of CBDC you can use for business and consumer transactions, such as paying for a supermarket purchase

wholesale CBDC vs retail CBDC - what's the difference?
there's two types of central bank digital currencies (CBDC): retail CBDC and wholesale CBDC
➖ retail CBDC = used for ordinary transactions. digital version of the cash
➖ wholesale CBDC = used for interbank/financial institution settlement. tokenized central bank reserves
wholesale CBDC vs retail CBDC - what's the difference?
there's two types of central bank digital currencies (CBDC): retail CBDC and wholesale CBDC
➖ retail CBDC = used for ordinary transactions. digital version of the cash
➖ wholesale CBDC = used for interbank/financial institution settlement. tokenized central bank reserves
retail CBDC is central bank money, so converting bank deposits into digital Euro changes the composition of the monetary base - fewer commercial bank reserves at the central bank, more central bank CBDC liabilities
retail CBDC conversions settle in reserves
ECB plans to limit the amount of digital Euro CBDC a wallet can hold
this means you will be limited the amount of digital EUR you can own
this applies only to retail European Central Bank CBDC, not wholesale. the idea is to prevent excessive outflows of deposits from banks
👉 Digital Money ≠ E-Money 👈
🏦 Digital Money - claim on central bank money recorded on a public ledger. A form of public money. No credit risk. Think CBDC
💳 E-Money - claim on commercial bank money. A form of private money. Has credit risk. Think PayPal balance
Read the full article to dive deeper into how the BRICS digital currency can be realized as a cryptocurrency on a public blockchain. 📖
🔗 https://illya.sh/blog/posts/brics-cryptocurrency-blockchain/
Let's discuss! Share your thoughts below🗣️

🌟 By embracing public blockchains and ZeroKnowledge technologies, the BRICS digital currency can pioneer a new era of finance🔮
A more efficient, interoperable, decentralized, and inclusive financial system aligned with Web3 principles 🌍
🌟 By embracing public blockchains and ZeroKnowledge technologies, the BRICS digital currency can pioneer a new era of finance🔮
A more efficient, interoperable, decentralized, and inclusive financial system aligned with Web3 principles 🌍

🧩 Implementing the BRICS currency on a public blockchain reduces cost & complexity
The dynamic supply is controlled by smart contracts, while ZKPs bridge data from arbitrary sources 🌉
Demand is driven by incentives for participating in the BRICS economic network 💰
🌍 The BRICS digital currency aims to integrate with existing monetary systems, creating a unified economic area for member nations 🤝
Its value is algorithmically derived from various economic factors of the participating countries 📈

🚀 BRICS Digital Currency: Cryptocurrency on a Public Blockchain 🪙
In this article, we explore how the BRICS currency can be implemented on a public blockchain and challenge the claims made in "Digital Money Options for the BRICS" for Web3
🚀 BRICS Digital Currency: Cryptocurrency on a Public Blockchain 🪙
In this article, we explore how the BRICS currency can be implemented on a public blockchain and challenge the claims made in "Digital Money Options for the BRICS" for Web3