Laptop as a Meshtastic LoRa Node Using ESP32, BLE and Python
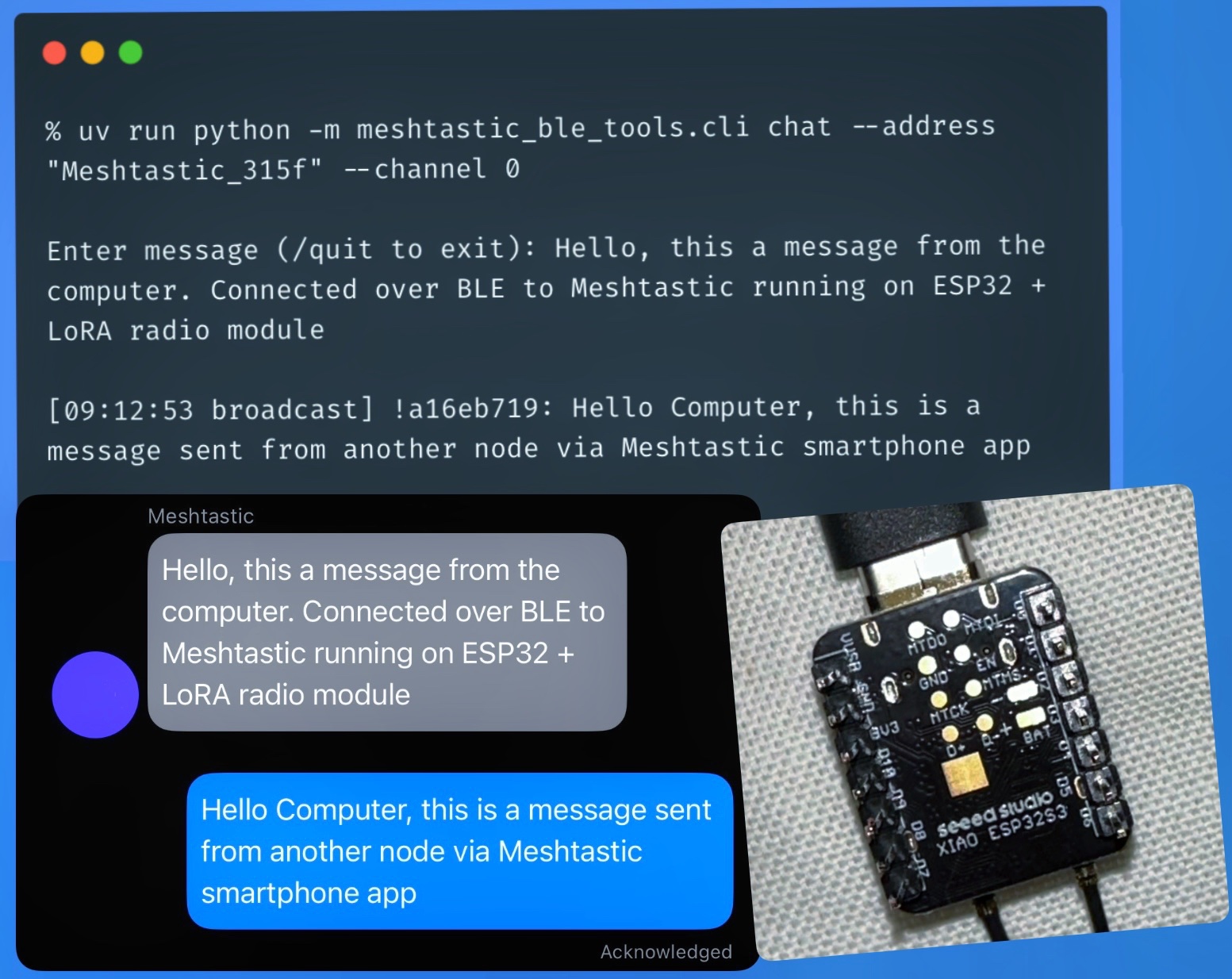
Meshtastic exposes a BLE interface and comes with a nice Python library. So I connected to the ESP32 with a LoRA module over bluetooth, and was able to send and receive messages from a Python script running on a laptop.
Essentially, the laptop uses the microcontroller as a proxy for the sub-GHz antenna (EU_868/≈868 MHz in Europe), enabling it to send and receive LoRa messages via Meshtastic's firmware. So effectively Bluetooth Low Energy is used as a proxy protocol for LoRa.
There were two nodes in the mesh - one connected to the laptop and another to a smartphone. Both nodes had the same channel name, Pre-Shared Key (PSK) and ordering (channel id) setup. The laptop node was using Python to connect to the mesh via BLE and exchange messages. The smartphone was connected to the other node, and the official Meshtastic app was used to send and receive messages.
The setup is as follows:
💻 Laptop (Python)
⇅ BLE
📡 Node A (ESP32 + LoRa)
≈≈≈ 868 MHz LoRa mesh ≈≈≈
📡 Node B (ESP32 + LoRa)
⇅ BLE
📱 Phone (Meshtastic app)
So you don't really need to program the ESP32 to make it a "smart" LoRa node. You can program all of the logic on your usual dev machine, and use BLE as a proxy for LoRa packets over Meshtastic. This is a great approach for iterative development, prototyping, proof of concepts and even final products. Of course, you can also put the smart node code on a Raspberry Pi, Arduino or even the microcontroller itself.