🚀 Exploring Tokenized Liquid Futures Contracts
Futures contracts serve crucial roles in finance:
1️⃣ Hedging against price volatility
2️⃣ Speculation on future asset prices
3️⃣ Price discovery for underlying assets
Smart contracts on the blockchain will disrupt this $1T+ market. Here's how ⬇️
🏦 Traditional futures require centralized clearing houses
On the blockchain, smart contracts eliminate intermediaries, enabling decentralized peer-to-peer agreements
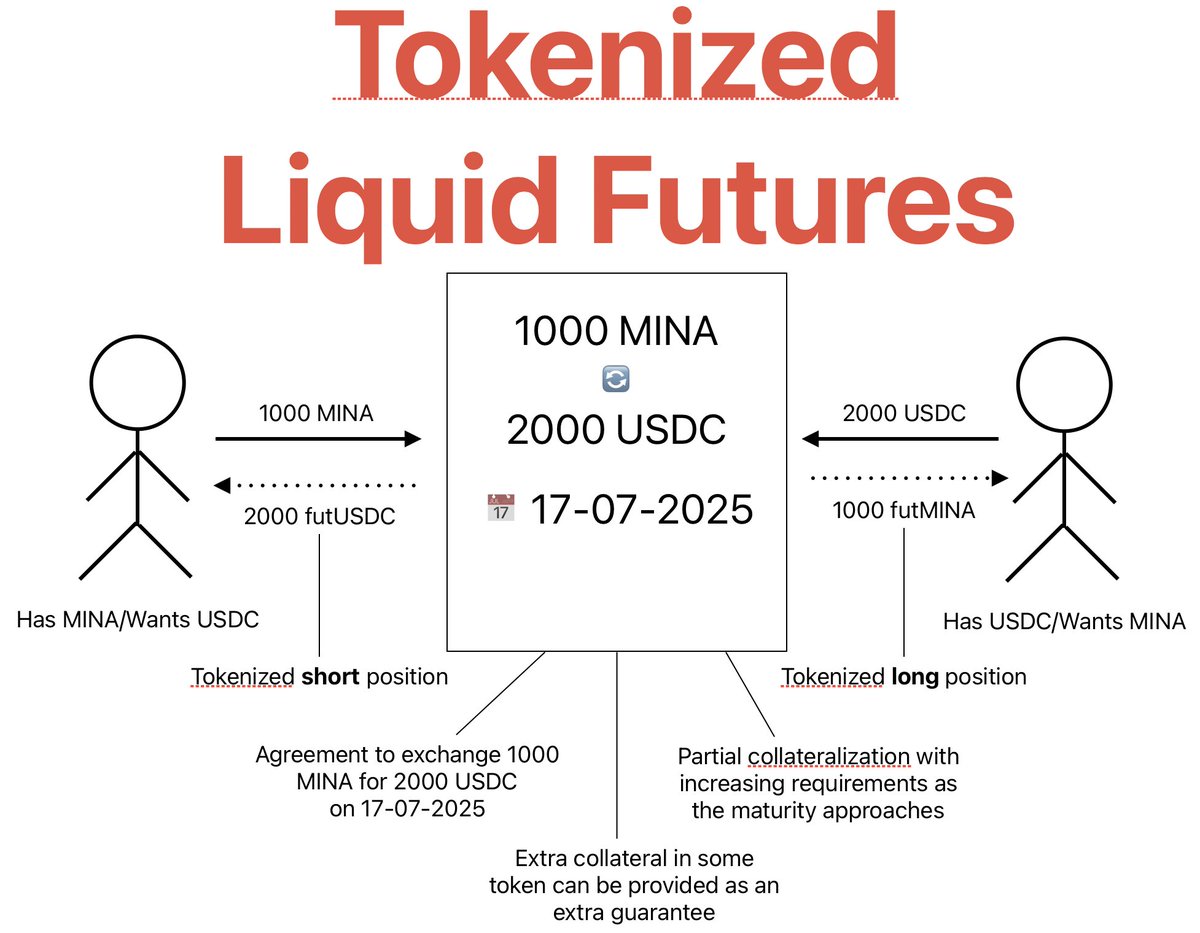
Example: A contract to trade 1000 $MINA for 2000 $USDC in 1 year, regardless of future $MINA price 📊
Futures pricing is deterministic, and its main goal is to prevent arbitrage:
💰 Futures Price = Spot Price * e^(rT)
- r: risk-free rate (e.g., $MINA staking yield)
- T: time to maturity
This formula approximates pricing at maturity in both TradFi and DeFi 🧮
🔐 Smart contracts on the blockchain enable full tokenization of futures contracts
📈 Both long and short positions become tokens, representing a "promise of future asset or money"
This allows partial selling of positions, increasing liquidity, flexibility and reducing risk 💧
Each position (long and short) is subdivided into several fungible tokens, which can be traded independently
The native token support of Mina Protocol blockchain means that a smart contract encodes both: the futures agreement, and its tokenization 🪙
The DeFi margin for futures contracts differs from TradFi margins, by:
1️⃣ Gradually increasing over time
2️⃣ Ensuring full collateralization by maturity
3️⃣ Delaying full payment
TradFi margin's main goal is to cover daily settlement gains/losses of the futures position
📈 The margin requirements increase algorithmically over the contract's lifespan
This ensurer both parties deposit their obligation in full by maturity, while allowing for partial collaterization
Thus leveraging the time value of money, without the need for a trusted party
Example of gradually increasing margin:
- Day 1: 10% deposit required
- Month 1: 25% required
- Month 2: 50% required
- Month 3 (Maturity): 100% required
This flexibility allows parties to structure payments based on future cash flows 💰
The margin in DeFi futures acts as:
1️⃣ Traditional margin, as in TradFi
2️⃣ Collateral hedging the counterparty risk
3️⃣ Under-collateralized assurance for a futures contract delivery
Daily/periodic settlement can be incorporated into the dynamic margin requirements
Smart contract on the blockchain tracks:
1️⃣ Deposited amounts for each party
2️⃣ Required deposits at each checkpoint
3️⃣ Maturity date
It uses this data to automatically enforce the increasing margin schedule 🔐
If a party fails to meet margin requirements, the smart contract:
1️⃣ Terminates the agreement
2️⃣ Transfers deposited assets to the compliant party
3️⃣ Applies penalties to the defaulting party
This liquidation process is executed automatically on-chain 🤖
🛟 The liquidation logic makes the initial required margin a collateral for all of the parties
Failure to meet the obligations means a loss of the deposited margin/collateral, either in full or in part
🕑 The later this default occurs, the higher this loss is to the offending party
This aligns with the principle of the time value of money
The tokenization of the long and the short positions of the futures contact allows for trading of the positions in a fully decentralized manner, without the need for need for a clearing house
This means no trusted entity or oracles are required, ensuring full decentralization
The smart contract automates risk management on-chain by:
1️⃣ Enforcing margin requirements
2️⃣ Handling liquidations
3️⃣ Ensuring contract settlement
Removing the need for trusted third parties and ensuring transparency 🛡️
In summary, blockchain-based Tokenized Liquid Futures:
- Eliminate intermediaries
- Increase transparency
- Enhance liquidity
- Automate risk management
- Provide flexible capital deployment
Thus enabling a disruptive #DeFi use-case over its #TradFi equivalent